
For POTEntial=HIGH, a restraining function for stereospecifically assignable proton pairs is employed (Habazettl et al. 1990). This is useful for resolved but unassigned peaks involving methylene protons. The restraining function is given by
where S is the energy constant specified
by the SCALe statement.
Supppose that one observes 2n distance restraints involving
the two protons a and b of a particular unassigned pair; this means
that there are a total of 2n ASSIgn statements specified for
this particular unassigned pair (NCOUnt has to match 2n).
The 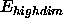 function is then the product of two 2n-dimensional functions, each
corresponding to one of the two possible stereospecific assignments:
function is then the product of two 2n-dimensional functions, each
corresponding to one of the two possible stereospecific assignments:

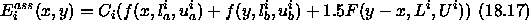
where 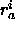 and
and 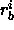 are the distances from spin
i to the unassigned spins a and b, respectively. When the
corresponding ASSIgn statements contain multiple atom selections,
averaged distances are computed; only center-averaging
is allowed in combination with the high dimensional potential.
are the distances from spin
i to the unassigned spins a and b, respectively. When the
corresponding ASSIgn statements contain multiple atom selections,
averaged distances are computed; only center-averaging
is allowed in combination with the high dimensional potential. 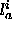 and
and
 are lower bounds for the distances between spin i and
spins a and b, respectively.
are lower bounds for the distances between spin i and
spins a and b, respectively. 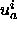 and
and
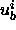 are upper bounds for the distances between spin i and
spins a and b, respectively.
are upper bounds for the distances between spin i and
spins a and b, respectively.  and
and
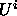 are the lower bounds and upper bounds for the distance
difference y-x, respectively. These
upper and lower bounds are specified through a group of 2n assignment
statements:
are the lower bounds and upper bounds for the distance
difference y-x, respectively. These
upper and lower bounds are specified through a group of 2n assignment
statements:

...
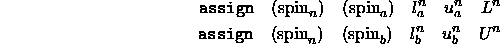
where the 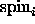 terms should be understood as atom selections.
terms should be understood as atom selections.
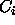 are constants that
are determined internally, such that the barrier height between
the two minima of
are constants that
are determined internally, such that the barrier height between
the two minima of 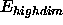 is given by BHIG.
The functional forms of f and F are
similar to the soft-square
function (Section 18.3.3) with a linear
asymptote, except that the
switching region is symmetrically arranged:
is given by BHIG.
The functional forms of f and F are
similar to the soft-square
function (Section 18.3.3) with a linear
asymptote, except that the
switching region is symmetrically arranged:
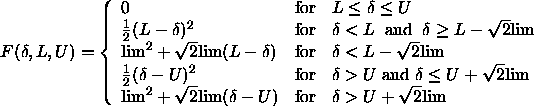
where lim is set internally to 0.1.