- <vector-mode> <vector-expression> <selection>
-
- DO
- manipulates atom properties. The operations are carried out component by component for all selected atoms.
- IDENtify
- is used to define and store an atom selection. The output array will contain the sequential number of the selected atoms or otherwise zero.
- SHOW <vector-show-property>
-
can be used to analyze atom properties.
- AVE
- shows the arithmetic average of selected elements and stores it in $RESULT.
- ELEMent
- shows selected elements and stores the last element in $RESULT.
- MAX
- shows the maximum of selected elements and stores it in $RESULT.
- MIN
- shows the minimum of selected elements and stores it in $RESULT.
- NORM
- shows the norm (
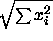 ) of selected elements and
stores it in $RESULT.
) of selected elements and
stores it in $RESULT.
- RMS
- shows the root-mean-square (rms) deviation

of selected elements and stores it in $RESULT.
- SUM
- shows the arithmetic sum of selected elements and
stores it in $RESULT.
- <atom-property>
- = <vector-operation> carries out the vector operation and assigns it to the specified atom property.
- <vector-operation>
- carries out the vector operation
without assigning the result to an
atom property. It should be used for the IDENtify
and SHOW vector modes.
- <vflc>
- [ <op> <vector-operation> ]
executes operators with the highest precedence first.
Operators with the same precedence are executed from left to right.
Operations have to be meaningful; i.e., the
data type of the operands has to match the operation. For strings,
only the ``+" and ``-" operations are allowed.
The following is a list of the operators
with increasing precedence:
- +
- denotes addition; concatenation for strings.
- -
- denotes subtraction; unary minus or negative concatenation for strings.

- denotes multiplication.

- denotes division.
- ^
- denotes exponentiation.
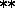
- denotes exponentiation (same as ^ ).
- <atom-property>
- | <function> |
<integer> | <real> | <string> | <symbol>
is a group of functions. Use of a string requires enclosure in double quotes`` ".
The data
type of the function arguments has to match the data type of the
operands.
- ABS(<vflc>)
- expects one argument and returns its absolute value. Argument restrictions: no string.
- ACOS(<vflc>)
- denotes arc cosine. Argument restrictions: no string or complex; expects argument in degrees.
- ASIN(<vflc>)
- denotes arc sine. Argument restrictions: no string or complex; expects argument in degrees.
- COS(<vflc>)
- denotes cosine. Argument restrictions: no string; expects argument in degrees.
- DECODE(<vflc>)
- converts a character string to a numerical number if possible.
- ENCODE(<vflc>)
- converts a numerical number to a character string.
- EXP(<vflc>)
- is an exponentiation function. Argument restrictions: no string.
- GAUSS(<vflc>)
- is a Gaussian distribution random-number function; it has one argument, the desired standard deviation. The mean of the distribution is always zero. Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- HEAVY(<vflc>)
- is a heavy-side function; it expects one real-number argument. If the argument is greater than zero, heavy returns a one; otherwise heavy returns a zero. Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- INT(<vflc>)
- is a truncation. Argument restrictions: no string.
- LOG10(<vflc>)
- is a natural log. Argument restrictions: no string or complex; argument must be greater than zero.
- LOG(<vflc>)
- is a logarithmic function. Argument restrictions: no string or complex; real numbers must be greater than zero, and the complex (0.0,0.0) is illegal.
- MAX(<vflc> {, <vflc> } )
- is a maximum-value function; it must have at least two arguments, and it returns the value of the argument with the maximum value. Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- MAXW(<vflc>)
- is a Maxwellian distribution random-number function; it has one argument, the desired standard deviation. The mean of the distribution is always zero. Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- MIN(<vflc> {, <vflc> })
- is a minimum-value function; it must have at least two arguments, and it returns the value of the argument with the minimum value. Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- MOD(<vflc>,<vflc>)
- returns the remainder of the first argument divided by the second. Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- NORM(<vflc>)
- is a normalization function; it has one argument, which must be a recognized variable. This function calculates the sum of the squares of all selected elements in the argument array. Then it divides each selected element by the square root of the sum of the squares. Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- RANDom()
- is a random-number function; it has no argument. It returns a uniform distribution between 0 and 1.
- SIGN(<vflc>)
- is a transfer of sign. If the argument is >= 0, it returns +1; if the argument is < 0, it returns -1. Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- SIN(<vflc>)
- denotes sine. Argument restrictions: no string; expects degrees.
- SQRT(<vflc>)
- returns the square root of the given argument. Argument restrictions: no string; no negative real numbers.
- TAN(<vflc>)
- denotes tangent in degrees.
Argument restrictions: no string or complex.
- B
- B-factors of main coordinate set in Å
 ( real)
( real)
- BCOMp
- B-factors of comparison coordinate set in Å
 ( real)
( real)
- CHARge
- electric charge in electronic charges ( real)
- CHEMical
- chemical atom type ( string)
- DX
- x component of first derivatives in
kcal mole
 Å
Å ( real)
( real)
- DY
- y component of first derivatives
in kcal mole
 Å
Å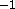 ( real)
( real)
- DZ
- z component of first derivatives
in kcal mole
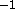 Å
Å ( real)
( real)
- FBETa
- friction coefficient in psec
 ( real)
( real)
- HARMonic
- energy constants of harmonic restraints in
kcal mole
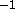 Å
Å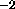 ( real)
( real)
- MASS
- mass in amu ( real)
- NAME
- atom name ( string)
- Q
- occupancies of main coordinate set ( real)
- QCOMp
- occupancies of comparison coordinate set ( real)
- REFX
- x component of reference coordinate set in Å ( real)
- REFY
- y component of reference coordinate set in Å ( real)
- REFZ
- z component of reference coordinate set in Å ( real)
- RESId
- residue number ( string)
- RESName
- residue name ( string)
- RMSD
- array used by various modules, e.g., the COOR RMS statement
- SEGId
- segment or chain identifier ( string)
- STORE1
- 1st internal store, is fragile ( real)
- STORE2
- 2nd internal store, is fragile ( real)
- STORE3
- 3rd internal store, is fragile ( real)
- STORE4
- 4th internal store, is fragile ( real)
- STORE5
- 5th internal store, is fragile ( real)
- STORE6
- 6th internal store, is fragile ( real)
- STORE7
- 7th internal store, is fragile ( real)
- STORE8
- 8th internal store, is fragile ( real)
- STORE9
- 9th internal store, is fragile ( real)
- VX
- x component of current velocities in Å psec
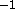 ( real)
( real)
- VY
- y component of current velocities in Å psec
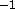 ( real)
( real)
- VZ
- z component of current velocities in Å psec
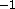 ( real)
( real)
- X
- x component of main coordinate set in Å ( real)
- XCOMp
- x component of comparison coordinate set in Å ( real)
- Y
- y component of main coordinate set in Å ( real)
- YCOMp
- y component of comparison coordinate set in Å ( real)
- Z
- z component of main coordinate set in Å ( real)
- ZCOMp
- z component of comparison coordinate set in Å
( real)