
Crystallographic symmetry interactions (e.g., packing interactions) between the molecule(s) located in the asymmetric unit and all symmetry-related molecules surrounding the asymmetric unit are computed by


where the first sum extends over all cystallographic symmetry operators
(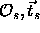 ) and
) and 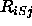 is defined by
is defined by
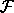 is the matrix that converts orthogonal coordinates into fractional
coordinates, and the second sum extends over all pairs of atoms
is the matrix that converts orthogonal coordinates into fractional
coordinates, and the second sum extends over all pairs of atoms 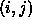 for
which
for
which 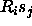 is less then a specified cutoff selected
by the constraints interaction statement
is less then a specified cutoff selected
by the constraints interaction statement
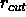 and
and  and
and 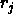 are the coordinates.
The function
are the coordinates.
The function  defines the minimum image distance in
fractional
coordinate space. It operates separately on each component of the
three-dimensional
vector
defines the minimum image distance in
fractional
coordinate space. It operates separately on each component of the
three-dimensional
vector 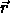 , where the operation on each component x is
given by
, where the operation on each component x is
given by
The function 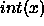 is defined as the integer part of x, and
is defined as the integer part of x, and 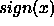 is
defined as the sign of x. The nonbonding interaction energy between two
atoms
is independent of whether it is an intermolecular or an intramolecular
interaction. The atom/group search and the update of the interaction list
are
carried out analogously to the intramolecular case. (Refer to
Section 12.3
for the definition of symmetry operators and the
unit-cell constants
that define
is
defined as the sign of x. The nonbonding interaction energy between two
atoms
is independent of whether it is an intermolecular or an intramolecular
interaction. The atom/group search and the update of the interaction list
are
carried out analogously to the intramolecular case. (Refer to
Section 12.3
for the definition of symmetry operators and the
unit-cell constants
that define  .)
.)