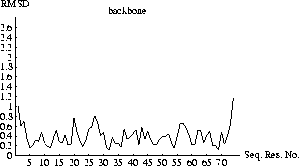
Figure 6.1: Rmsd vs. residue number.
The following example shows how to compute all rms differences (rmsd) between two coordinate sets (one in the main set, one in the comparison set). The rmsds are rms-averaged over all atoms of each residue. The user is also referred to Sections 20.8 and 20.9 for computation of averages and rmsds of a family of coordinate sets.
X-PLOR produces the file ``rmsdplot.list", which can be interpreted by Mathematica:
The resulting plots of the rmsds as a function of sequential residue number are shown in Figs. 6.1 and 6.2.

Figure 6.1: Rmsd vs. residue number.
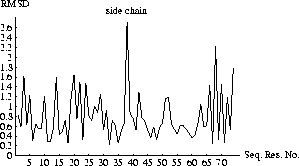
Figure 6.2: Rmsd vs. residue number.
The correspondence between sequential residue number and actual residue identifier can be established by using vector statements (see Section 5.4).