Next: Turning Energy Terms
Up: Energy Function
Previous: Non-crystallographic Symmetry Interactions
The explicit hydrogen-bond energy term 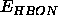 is used in certain
parameter sets, in particular the ones that deal with nucleic acids.
In the more recent protein parameter files,
this term is zero, and the effect
of hydrogen bonds is taken implicitly into account by appropriate
parameterization of the partial charges and van der Waals parameters.
The explicit hydrogen-bond term has the form
is used in certain
parameter sets, in particular the ones that deal with nucleic acids.
In the more recent protein parameter files,
this term is zero, and the effect
of hydrogen bonds is taken implicitly into account by appropriate
parameterization of the partial charges and van der Waals parameters.
The explicit hydrogen-bond term has the form
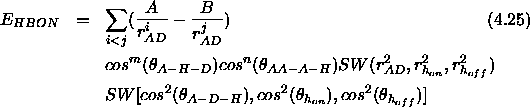
involving atoms AA, A, H, D (acceptor antecedent, acceptor,
hydrogen, and donor heavy atom), where i, j, m, and n are positive
integers and SW
is the switching function defined in Eq. 4.9.
The switching function SW
maintains a continuous and smooth function
to the cutoff point so that derivatives are well defined at
the cutoff point.
The sum in Eq. 4.25 extends over all pairs of donors and
acceptors (DONOr
and ACCEptor statements;
see Section 3.1.1) for which
the donor-acceptor distance and the donor-hydrogen-acceptor angle
satisfy the
criteria specified by DCUT and ACUT
(see Section 3.2.1).
AEXP assigns the j exponent, REXP assigns the i exponent,
AHEX assigns the m exponent, and AAEX assigns the n
exponent;
A and B are defined by the HBON statement
(see Section 3.2.1). The remaining switching parameters are
provided by the hbonds statement. The computational time
for searching for hydrogen bonds that satisfy the cutoff criteria
is reduced by introducing an approximation, storing the
atomic pair
indices (i<j) that satisfy the cutoff criteria in a list that is updated
only when any atom has moved more than the value specified by
TOLErance.
Web Manager
Sat Mar 11 09:37:37 PST 1995
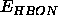 is used in certain
parameter sets, in particular the ones that deal with nucleic acids.
In the more recent protein parameter files,
this term is zero, and the effect
of hydrogen bonds is taken implicitly into account by appropriate
parameterization of the partial charges and van der Waals parameters.
The explicit hydrogen-bond term has the form
is used in certain
parameter sets, in particular the ones that deal with nucleic acids.
In the more recent protein parameter files,
this term is zero, and the effect
of hydrogen bonds is taken implicitly into account by appropriate
parameterization of the partial charges and van der Waals parameters.
The explicit hydrogen-bond term has the form