




Next: Conventional Positional Refinement
Up: Positional Refinement
Previous: Positional Refinement
This procedure checks the initial R value and determines the ideal
weight 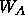 (and
(and 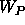 if a phase restraint is used)
between
if a phase restraint is used)
between 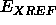 and
and  . The procedure
should be carried out before running
any refinement on the system. The weight
. The procedure
should be carried out before running
any refinement on the system. The weight 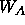 is determined by running a
brief molecular dynamics calculation without
is determined by running a
brief molecular dynamics calculation without 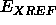 and then comparing the norm of the gradient of
and then comparing the norm of the gradient of  and the norm of the gradient of
and the norm of the gradient of 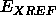 .
The program will display the weight. A similar procedure should be
applied when using targets other than the crystallographic
residual (Eq. 12.1).
.
The program will display the weight. A similar procedure should be
applied when using targets other than the crystallographic
residual (Eq. 12.1).
check.inp
If the minimizer exits with ``line search abandoned" and
very large van der Waals energies (in the thousands of
kcal mole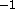 ), the
structure probably has bad contacts. The output of
X-PLOR provides a list of bad contacts
.
One should check the molecule and symmetry-related molecules on
the graphics and fix the problem. If this is inconvenient,
try the following procedure:
use the ``repel" nonbonded energy
function (see Section 4.1) for
the first several steps of minimization. One should
replace the minimization statement in the example above
with the following statements:
), the
structure probably has bad contacts. The output of
X-PLOR provides a list of bad contacts
.
One should check the molecule and symmetry-related molecules on
the graphics and fix the problem. If this is inconvenient,
try the following procedure:
use the ``repel" nonbonded energy
function (see Section 4.1) for
the first several steps of minimization. One should
replace the minimization statement in the example above
with the following statements:
parameter nbonds repel=0.89 rcon=4. end end
{*This turns on the repulsive *}
{*function. *}
minimize powell
nstep=40
drop=40.0
end
{* This switches back to the Lennard-Jones function.*}
parameter nbonds repel=0.0 end end
minimize powell
nstep=40
drop=40.0
end
Web Manager
Sat Mar 11 09:37:37 PST 1995
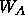 (and
(and 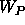 if a phase restraint is used)
between
if a phase restraint is used)
between 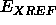 and
and  . The procedure
should be carried out before running
any refinement on the system. The weight
. The procedure
should be carried out before running
any refinement on the system. The weight 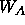 is determined by running a
brief molecular dynamics calculation without
is determined by running a
brief molecular dynamics calculation without 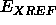 and then comparing the norm of the gradient of
and then comparing the norm of the gradient of  and the norm of the gradient of
and the norm of the gradient of 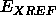 .
The program will display the weight. A similar procedure should be
applied when using targets other than the crystallographic
residual (Eq. 12.1).
.
The program will display the weight. A similar procedure should be
applied when using targets other than the crystallographic
residual (Eq. 12.1).
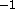 ), the
structure probably has bad contacts. The output of
X-PLOR provides a list of bad contacts
), the
structure probably has bad contacts. The output of
X-PLOR provides a list of bad contacts